We are developing a new version of Tumor Portal. You can go there and give us some feedback.
External References:
Wikipedia
GeneCards
HUGO
COSMIC
Google Scholar
NCBI Description of BRCA1 |
| This gene encodes a nuclear phosphoprotein that plays a role in maintaining genomic stability, and it also acts as a tumor suppressor. The encoded protein combines with other tumor suppressors, DNA damage sensors, and signal transducers to form a large multi-subunit protein complex known as the BRCA1-associated genome surveillance complex (BASC). This gene product associates with RNA polymerase II, and through the C-terminal domain, also interacts with histone deacetylase complexes. This protein thus plays a role in transcription, DNA repair of double-stranded breaks, and recombination. Mutations in this gene are responsible for approximately 40% of inherited breast cancers and more than 80% of inherited breast and ovarian cancers. Alternative splicing plays a role in modulating the subcellular localization and physiological function of this gene. Many alternatively spliced transcript variants, some of which are disease-associated mutations, have been described for this gene, but the full-length natures of only some of these variants has been described. A related pseudogene, which is also located on chromosome 17, has been identified. |
Community Annotation of BRCA1 Add / Edit BRCA1: Annotations
Added by
0
Added by
0 |
|
Figure notes
• "Mouse over" a mutation to see details. |
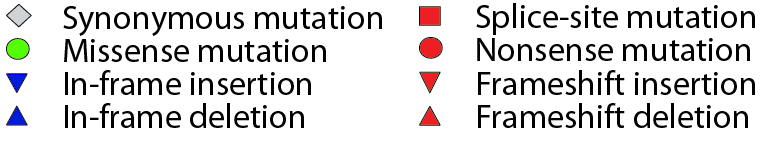
|
Click on a tumor type to see its full list of significant genes.
Data details