We are developing a new version of Tumor Portal. You can go there and give us some feedback.
External References:
Wikipedia
GeneCards
HUGO
COSMIC
Google Scholar
NCBI Description of SMC1A |
| Proper cohesion of sister chromatids is a prerequisite for the correct segregation of chromosomes during cell division. The cohesin multiprotein complex is required for sister chromatid cohesion. This complex is composed partly of two structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC) proteins, SMC3 and either SMC1L2 or the protein encoded by this gene. Most of the cohesin complexes dissociate from the chromosomes before mitosis, although those complexes at the kinetochore remain. Therefore, the encoded protein is thought to be an important part of functional kinetochores. In addition, this protein interacts with BRCA1 and is phosphorylated by ATM, indicating a potential role for this protein in DNA repair. This gene, which belongs to the SMC gene family, is located in an area of the X-chromosome that escapes X inactivation. |
Community Annotation of SMC1A Add / Edit SMC1A: Annotations
No community annotations yet for SMC1A.
|
|
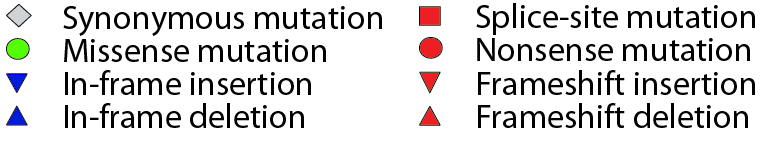
Figure notes
• "Mouse over" a mutation to see details. |
|
Click on a tumor type to see its full list of significant genes.
Data details