We are developing a new version of Tumor Portal. You can go there and give us some feedback.
External References:
Wikipedia
GeneCards
HUGO
COSMIC
Google Scholar
NCBI Description of RXRA |
| Retinoid X receptors (RXRs) and retinoic acid receptors (RARs), are nuclear receptors that mediate the biological effects of retinoids by their involvement in retinoic acid-mediated gene activation. These receptors exert their action by binding, as homodimers or heterodimers, to specific sequences in the promoters of target genes and regulating their transcription. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily of transcriptional regulators. |
Community Annotation of RXRA Add / Edit RXRA: Annotations
No community annotations yet for RXRA.
|
|
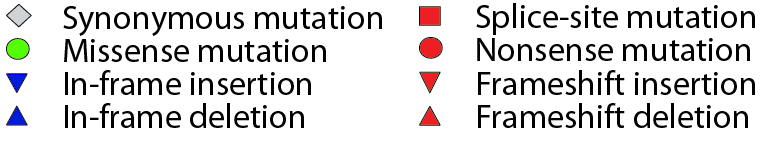
Figure notes
• "Mouse over" a mutation to see details. |
|
Click on a tumor type to see its full list of significant genes.
Data details