We are developing a new version of Tumor Portal. You can go there and give us some feedback.
External References:
Wikipedia
GeneCards
HUGO
COSMIC
Google Scholar
NCBI Description of BHMT2 |
| Homocysteine is a sulfur-containing amino acid that plays a crucial role in methylation reactions. Transfer of the methyl group from betaine to homocysteine creates methionine, which donates the methyl group to methylate DNA, proteins, lipids, and other intracellular metabolites. The protein encoded by this gene is one of two methyl transferases that can catalyze the transfer of the methyl group from betaine to homocysteine. Anomalies in homocysteine metabolism have been implicated in disorders ranging from vascular disease to neural tube birth defects such as spina bifida. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. |
Community Annotation of BHMT2 Add / Edit BHMT2: Annotations
No community annotations yet for BHMT2.
|
|
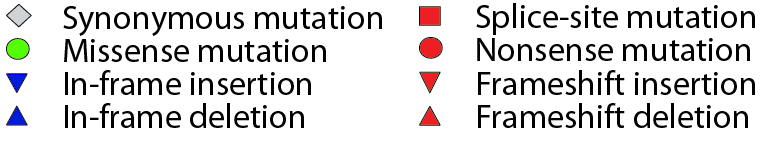
Figure notes
• "Mouse over" a mutation to see details. |
|
Click on a tumor type to see its full list of significant genes.
Data details