We are developing a new version of Tumor Portal. You can go there and give us some feedback.
External References:
Wikipedia
GeneCards
HUGO
COSMIC
Google Scholar
NCBI Description of ATP6V1C1 |
| This gene encodes a component of vacuolar ATPase (V-ATPase), a multisubunit enzyme that mediates acidification of intracellular compartments of eukaryotic cells. V-ATPase dependent acidification is necessary for such intracellular processes as protein sorting, zymogen activation, receptor-mediated endocytosis, and synaptic vesicle proton gradient generation. V-ATPase is composed of a cytosolic V1 domain and a transmembrane V0 domain. The V1 domain consists of three A and three B subunits, two G subunits plus the C, D, E, F, and H subunits. The V1 domain contains the ATP catalytic site. The V0 domain consists of five different subunits: a, c, c', c'', and d. Additional isoforms of many of the V1 and V0 subunit proteins are encoded by multiple genes or alternatively spliced transcript variants. This gene is one of two genes that encode the V1 domain C subunit proteins and is found ubiquitously. This C subunit is analogous but not homologous to gamma subunit of F-ATPases. Previously, this gene was designated ATP6D. |
Community Annotation of ATP6V1C1 Add / Edit ATP6V1C1: Annotations
No community annotations yet for ATP6V1C1.
|
|
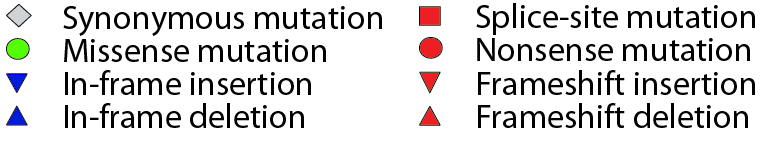
Figure notes
• "Mouse over" a mutation to see details. |
|
Click on a tumor type to see its full list of significant genes.
Data details